
17% of the depreciable base in year one). Because goodwill and some intangible assets will no longer be amortized. 17,000 miles driven in year one) to determine what proportion to depreciation (i.e. indicated that they did not regard goodwill amortization expense as being. Each year, it assesses its actual use (i.e. For example, a company buys a company vehicle and intends on driving it 100,000 miles. Therefore, the amortization expense journal entries for the loan will be as follows. Units of Production: A company assesses a baseline of anticipated usage. The entry would include a debit to amortization expense and a credit to the accumulated amortization or intangible asset account.Then, a company depreciates a proportion of costs based on the corresponding digit (i.e. an asset with a useful life would add up to 5+4+3+2+1 = 15 years). Sum-of-the-Years' Digits Method: The digits of the asset's useful life are summed (i.e.

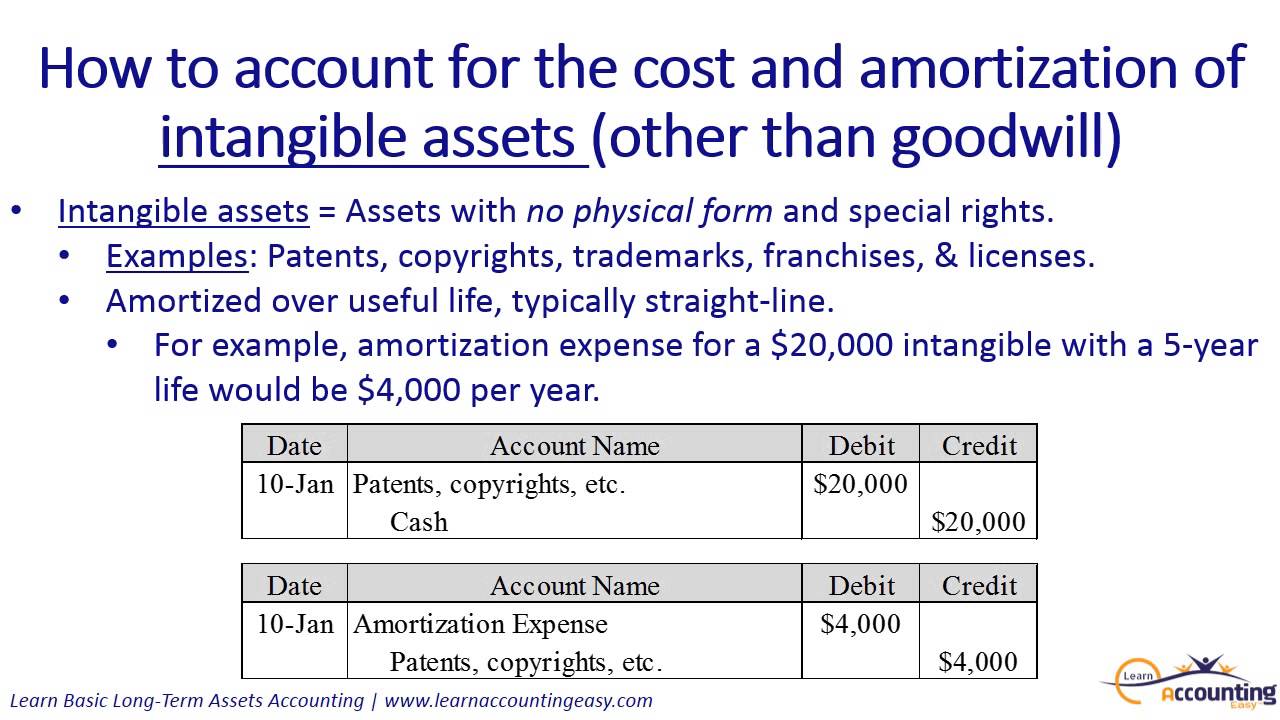
This rate is then applied to the current book value. Double Declining Balance Method: A company depreciates an accelerated amount of depreciation earlier in the asset's useful life by doubling the rate under the straight-line method.It is accounted for when companies record the loss in value of their fixed assets through depreciation. A portion of an intangible assets cost is allocated to each. Depreciation expense is an income statement item. The offsetting entry is a balance sheet account, accumulated amortization, which. Amortization is the systematic write-off of the cost of an intangible asset to expense. This is done by multiplying the current book value of the asset by a fixed depreciation rate that does not change over the life of the asset. Amortization expense is an income statement account affecting profit and loss. Amortization is used for non-physical assets called intangibles. Business assets are property owned by a business that is expected to last more than a year. Declining Balance: A company depreciates an accelerated amount of depreciation earlier in the asset's useful life. The concept of both depreciation and amortization is a tax method designed to spread out the cost of a business asset over the life of that asset.The same amount of depreciation is recorded each year. The depreciable base is determined by taking the asset's cost and reducing the salvage value. Straight-Line Method: A company depreciates the asset equally over the term of its useful life.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
